Canada
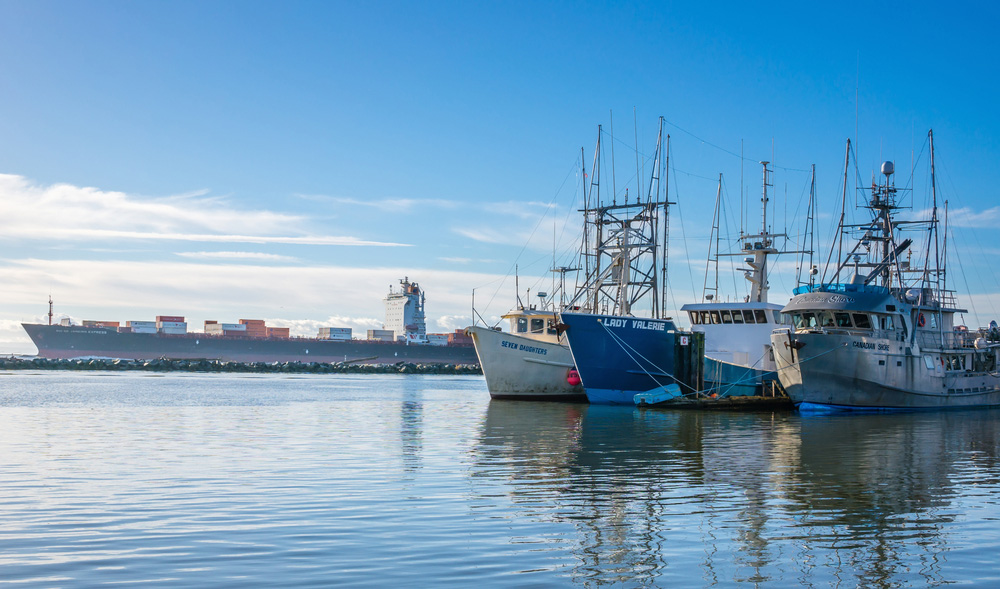

Canada's Fishing Industry
Out of Canada's primary industries, the fishing industry holds great significance in terms of catching and exporting fish. Canada exports more than 75% of its fishing and seafood production all over the world, it is estimated Canada exports to. Canada's fishing industry makes more than 5 billion dollars yearly. The fishing industry provides more than 130,000 jobs. Fishing and aquaculture industries operate in three regions, the Atlantic (East Coast), the Pacific (West Coast), and Freshwaters.
Canada's coastlines have always been highly valued but some issues need to be addressed. Fishing fleets from other countries have overfished Canada's waters which led to a sharp decline in species populations. Since then Canada has made efforts to regenerate the fish stocks we lost. Species like tuna, cod, and salmon are slowly returning. Key-word slowly. Fish populations are not regenerating as fast as we hoped. Species like Sockeye Salmon, Atlantic Bluefin Tuna, and Atlantic Cod are endangered.
Canada has been working towards sustainable fishing for several years now. Canada is one of the first countries in the world to protect fish stocks and aquatic habitats by developing its code of conduct for fisheries across the country. The science behind aquaculture is vital to understanding how we can become more sustainable. New technology has come to light that has improved the efficiency and decreased the wastefulness of fishing.

History of the Canadian Fishing Industry
Canada is very fortunate to be surrounded by the Atlantic, Pacific, and Arctic Oceans as well as having access to the Great Lakes, the fisheries located on the east and west coasts have always been an important resource for the country. The Canadian fishing industry can be traced back to the European settlers who arrived in Canada. The settlers harvested seafood to survive their trip back to Europe. French, English, Spanish, and Portuguese were the first settlers to begin fishing in Canada around the 16th century. The American Revolution caused the British to become more reliant on the East Coast fisheries (Newfoundland) to sustain their troops. The increase in demand led to the growth of the Atlantic economy and the permanent establishment of communities that focused on seafood harvesting and production.
After the Confederation was formed in 1867, the federal government of Canada established a Department of Marine and Fisheries to oversee the country's fishing industry and aquaculture resources. 50 years after the creation of the Confederation the Department of Marine and Fisheries developed facilities in the Atlantic provinces to increase the amount of fish they were bringing in. During the Second World War, modern technology and communication devices like radios, sonar, nylon nets, and hydraulic-powered equipment were widely adopted into fisheries across Canada which led to fishing vessels being more accurate and efficient. Since then the fishing industry has grown an enormous amount and we are now combating the issue of overfishing. The Cod fishery in the 1990s is an example of Canada's overfishing problem, the Cod population was permanently damaged, and the damage was caused because of the high catch rate of cod versus how fast the cod could reproduce.
Endangered Canadian Fish
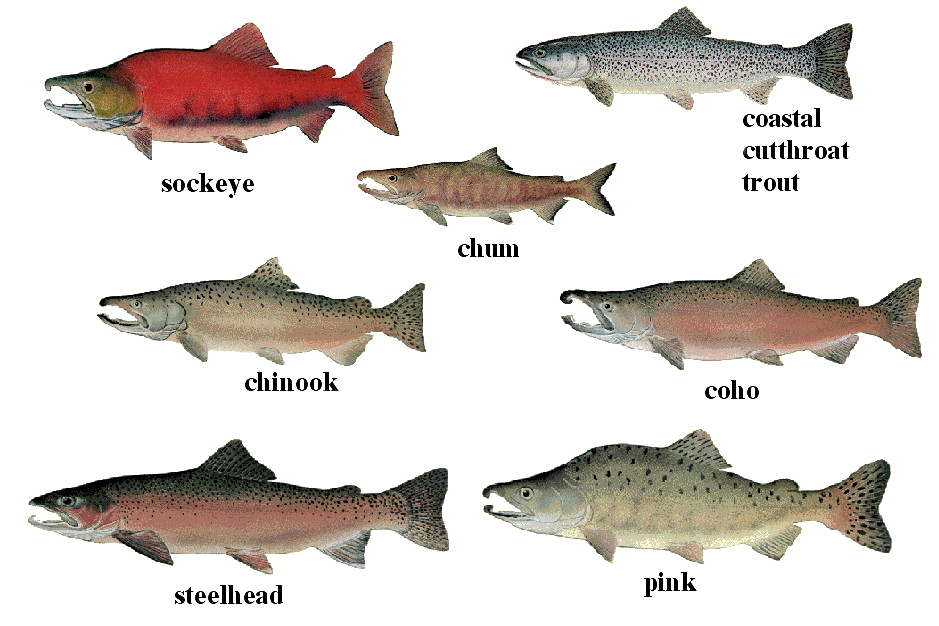
Salmon Species
Salmon is one of the most valuable fish that Canada exports. The most valued species is the sockeye salmon. Salmon are currently endangered because of commercial fishing changes in their habitat and climate change. These three main reasons have led to a decline in salmon populations across the country.
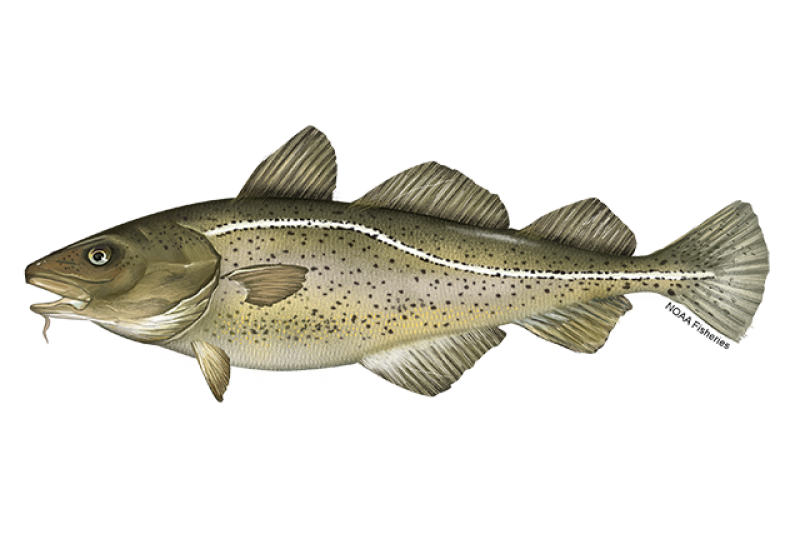

Atlantic Cod
Atlantic cod is a species that is directly impacted by overfishing. Overfishing is the main reason for their endangered status in Canada. Organizations like us are working towards rebuilding the Atlantic cod population.
Tuna Species
Tuna are very prized fish, because of their size,difficulty to catch and great taste. Bluefin tuna specifically is endangered because of overfishing as well as illegal fishing. they are illegally caught because of the high demand from the sushi market.
